Data Science explained
Date:
Changed on 06/05/2024

Every day, more than 200 billion emails are exchanged, 4 billion videos are seen on YouTube, 5.5 billion searches are made on Google, 4 billion messages are exchanged on Facebook and more than 500 million tweets are sent. These figures, which may seem impressive, are only a tiny part of the data generated every day in the world, by smartphones, bank cards, GPS, connected objects and other sensors present in our daily lives.
The development of new technologies, the Internet and social networks over the last twenty years has led to two problems: the storage of this gigantic volume of digital data produced, but also its sorting, analysis and proper use.
It is on the latter that the actors of data science are working, a field at the crossroads of statistics and computer science, which consists of exploiting large data sets containing structured and unstructured data and identifying hidden patterns to extract exploitable information. Data science also uses complex machine learning algorithms to build predictive models.
Why is this important?
Data is meaningless until it is converted into useful information. By collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data, data science today enables the understanding of the workings of many industries, no matter how complex and complicated.
Data science reveals trends and generally enables and facilitates decision making.
Data science employs techniques and theories drawn primarily from mathematics, statistics, and information technology. In particular, it exploits several interrelated technologies such as:
Data science has found applications in almost every industry. From cost savings to smoother processes and workflows to more effective risk management, better supply chain performance, and improved patient outcomes, data science is now enabling players across industries to make great strides, especially in terms of accuracy and efficiency. However, some sectors are now more impacted by the evolution of data management. Here are three examples:
Unsurprisingly, the healthcare sector is reaping huge benefits from the application of data science to medical thinking. Mining and analyzing existing data is now building a more accurate picture of patients, consumers and clinicians. Data-driven decision making opens up new opportunities to boost the quality of healthcare, including risk identification, new drug development, or personalization of treatments based on patient profiles.
Between production optimization, cost reduction and autonomy development, data science applied to industries offers a real added value to its actors. Based on existing data, mainly from the Internet of Things, data science allows companies to predict potential problems, monitor systems and analyze the continuous flow of data. This allows companies to reduce their energy costs and optimize their production hours.
Data science is also being used by logistics companies to optimize routes to ensure faster delivery of products and increase operational efficiency.
Read: EDGE Team: Towards new tools for decision support
Another important application of data science is mobility. The growing demand for a more comfortable, efficient, and cleaner transportation experience has indeed created tremendous pressure on operations and maintenance activities in the mobility sector in recent years.
Through in-depth analysis of fuel consumption patterns, driver behavior and active vehicle monitoring, data science is a solid answer to the transportation industry's problems, making driving environments safer for drivers, optimizing vehicle performance, but also creating better logistics routes for professional mobility players (rail, air, sea...).
More recently, data science has enabled the introduction and development of self-driving cars, for ever more precise use.
At Inria, several project teams are currently specialized in data science.
At the Inria center at the University of Bordeaux, these include Pleiade, Edge, Astral, HiePACS, Geostat, which has developed tools for processing big data, and Sistm and Monc, both of which focus on the health sector. The objective of the LACODAM team in Rennes is to considerably facilitate the process of making sense from large quantities of data, either for deriving new knowledge or for taking better actions.
At the Inria research center at Université Côte d'Azur, we can cite Maasai, Wimmics, Zenith and Lemon, which, for example, is developing theoretical and numerical tools (both deterministic and stochastic) to model coastal zone processes, whether inland or at sea.
Magnet, Spirals, Modal, all three based at the Inria center at the University of Lille, are also working on data analysis and management, as are Cedar at the Inria center in Saclay, and Valda, Heka, Aramis and Sierra at the Inria center in Paris.

How can we help journalists verify facts more quickly from data available online? This is the question Ioana Manolescu, director of the Cedar research team, has been working on.
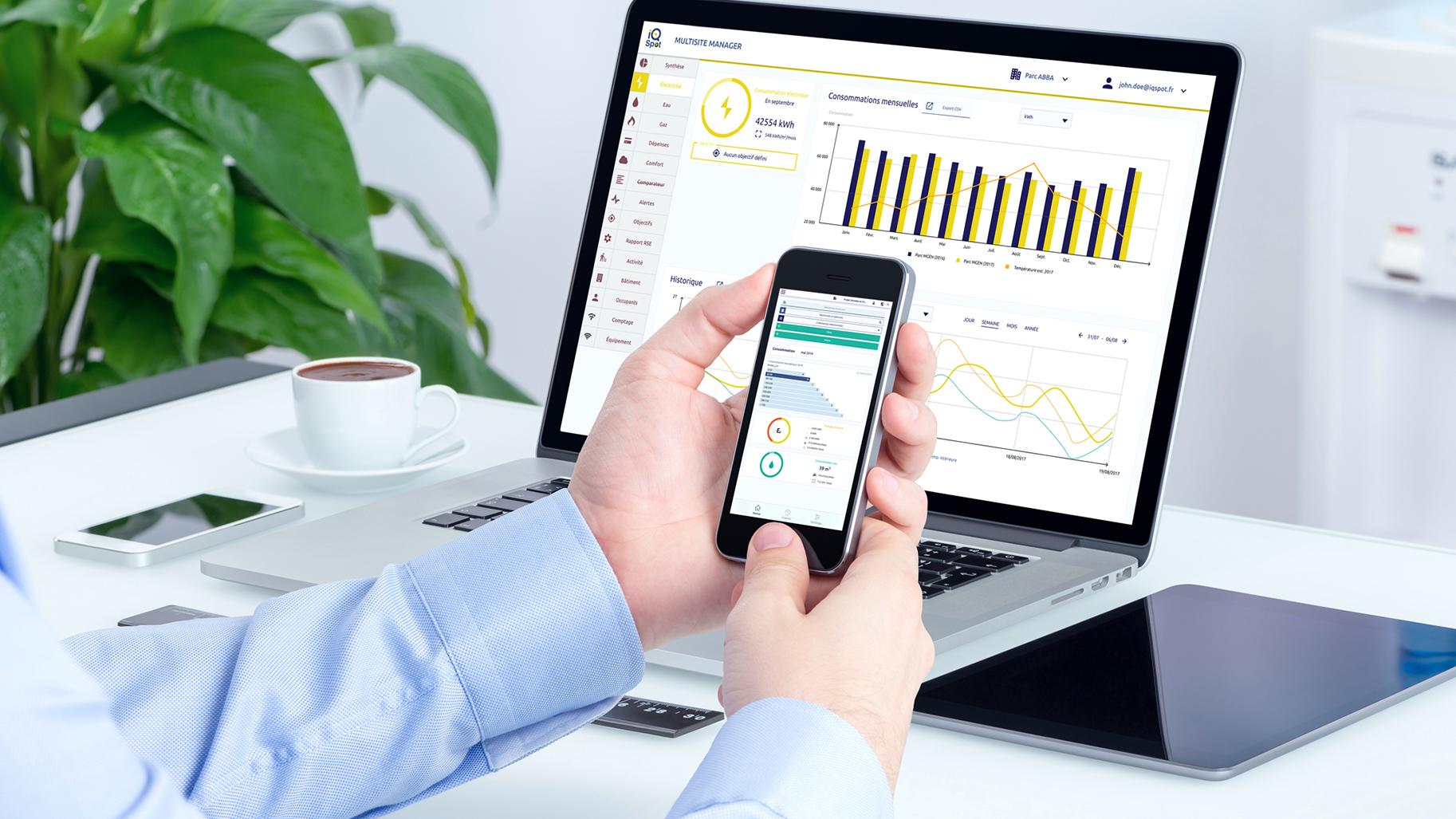
Founded in 2015, the startup works on the energy transition in the field of professional real estate, offering a solution for automatic collection and real-time analysis of real estate energy consumption.

The HistorIA project has led to the publication and availability, in 2020, of a system for computing groups (clusters) within a social network that relies on the sharing of initiatives between algorithms and the researcher's knowledge.

A multidisciplinary research team has unveiled the results of its research to identify the risk factors for dementia due to Alzheimer's disease. Its originality? It is based on the analysis of the medical records of nearly 80,000 patients consulting general practitioners in France and the United Kingdom.